Mastering Financial Inventory Tracking in Dynamics 365 Finance & Operations
Let us have an Introduction to Financial Inventory Management. Financial inventory tracking in Microsoft Dynamics 365 Finance and Operations represents a cornerstone of modern enterprise resource planning. This sophisticated functionality enables organizations to maintain precise control over their inventory valuations, cost management, and financial reporting across various organizational hierarchies. Understanding its intricacies is crucial for businesses seeking to optimize their supply chain operations and financial control mechanisms.
Understanding the Core Architecture
The Site Level Framework
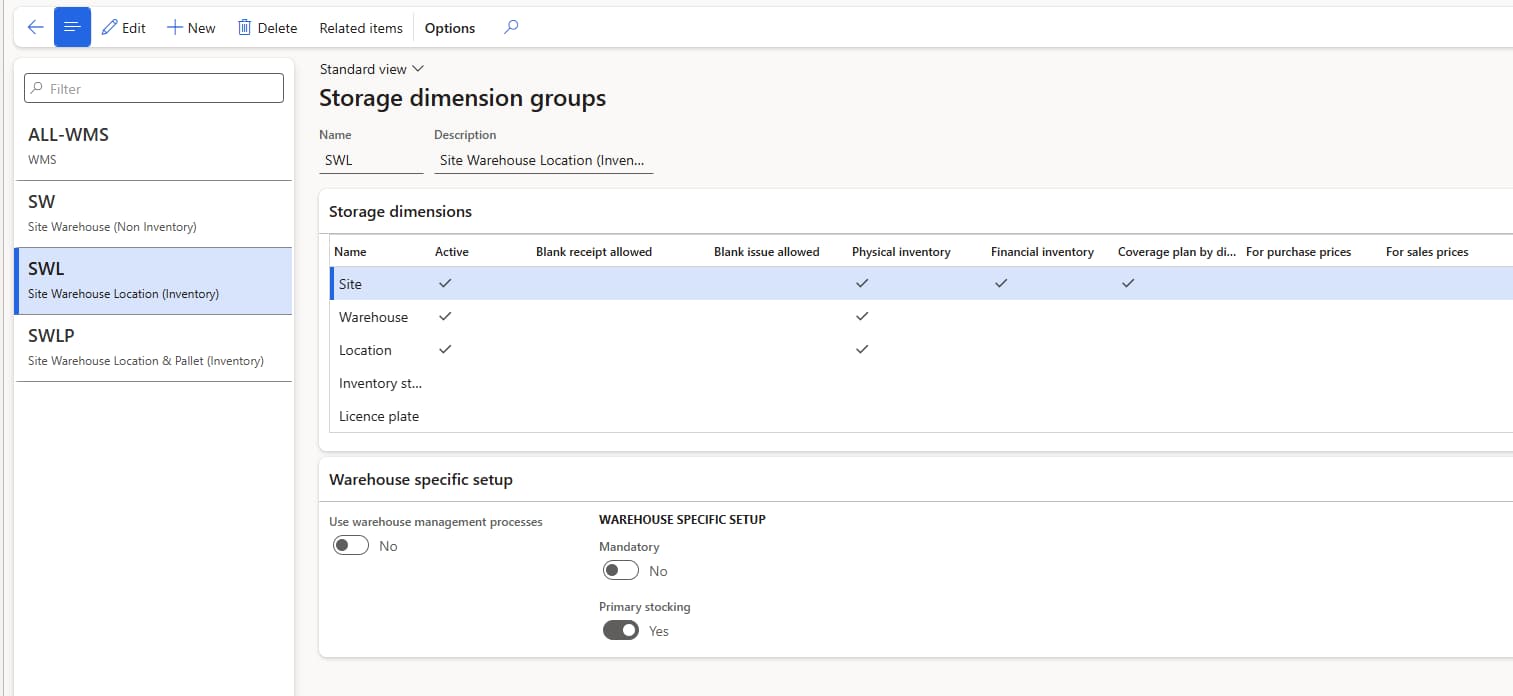
At the foundation of D365 FO’s inventory management lies the site level tracking system. This primary tier serves as the backbone of financial inventory control, where organizations can implement comprehensive cost tracking mechanisms. Sites typically represent physical facilities or distinct operational units within the organization. When financial tracking is enabled at this level, it facilitates:
Independent cost center management for each facility
Segregated financial reporting capabilities
Distinct inventory valuation methodologies
Site-specific cost of goods sold calculations
Automated financial posting patterns
Warehouse Level Integration
The warehouse level represents the second tier in the storage dimension hierarchy. While the image shows physical inventory tracking enabled without financial tracking at this level, it’s essential to understand its role in the broader ecosystem. Warehouses function as organizational units within sites, enabling:
Detailed stock location management
Inventory movement tracking
Storage capacity optimization
Internal transfer management
Resource allocation efficiency
Location Level Precision
The location level provides the most granular control over inventory management. As shown in the configuration, while physical tracking is enabled, financial tracking remains at the site level. This arrangement offers:
Precise item placement tracking
Optimized picking and putting away processes
Enhanced inventory accuracy
Improved warehouse efficiency
Streamlined order fulfillment
Advanced Implementation Strategies
System Integration Considerations
The successful implementation of financial inventory tracking requires careful attention to system integration aspects. The platform seamlessly connects with various modules:
General Ledger Integration
The system automatically generates appropriate accounting entries based on inventory movements and valuations. This integration ensures financial accuracy and maintains audit trails for all transactions.
Cost Accounting Framework
The cost accounting module leverages financial inventory tracking data to provide detailed cost analysis and profitability reporting. This integration enables organizations to:
Monitor product costs effectively
Analyze profitability by dimension
Track variance analysis
Generate accurate financial statements
Implement cost control measures
Performance Optimization Techniques
To maintain optimal system performance while managing financial inventory tracking:
Regular System Maintenance
Implementing scheduled maintenance routines ensures system efficiency and data accuracy. This includes:
Database optimization
Transaction log management
Data archiving strategies
Performance monitoring
System health checks
Business Process Impact
Operational Excellence
The implementation of financial inventory tracking significantly impacts daily operations:
Purchase Management
The system enables precise tracking of:
- Purchase order processing
- Goods receipt documentation
- Invoice matching procedures
- Vendor payment management
- Purchase price variances
Sales Operations
Enhanced control over:
- Order fulfillment tracking
- Revenue recognition
- Customer invoicing
- Shipment documentation
- Sales price management
Financial Control Mechanisms
The platform provides robust financial control features:
Cost Management
Detailed cost tracking enables:
- Standard cost maintenance
- Actual cost monitoring
- Variance analysis
- Cost allocation procedures
- Budget control mechanisms
Reporting Capabilities
Comprehensive reporting features include:
- Financial statements by dimension
- Inventory valuation reports
- Cost analysis documentation
- Audit trail reporting
- Performance metrics
Implementation Best Practices
Configuration Guidelines
Successful implementation requires adherence to proven configuration principles:
Dimension Setup
Careful consideration of dimension hierarchy ensures:
- Proper cost flow
- Accurate financial reporting
- Efficient operational processes
- Clear organizational structure
- Effective control mechanisms
Security and Control
Implementing proper security measures ensures:
Access Control
- Role-based security
- Transaction authorization levels
- Audit trail maintenance
- Data integrity protection
- System security protocols
Future Considerations
Scalability Planning
Organizations must consider future growth when implementing financial inventory tracking:
System Expansion
Planning for:
- Additional sites
- New warehouses
- Extended functionality
- Enhanced reporting
- Integration capabilities
Technology Evolution
Staying current with system updates and new features:
Platform Updates
Regular evaluation of:
- New functionality
- System improvements
- Performance enhancements
- Integration capabilities
- Security updates
Conclusion
Financial inventory tracking in Dynamics 365 Finance and Operations represents a crucial component of modern business operations. The system’s ability to manage complex inventory scenarios while maintaining financial accuracy makes it an invaluable tool for organizations seeking to optimize their operations. Through careful implementation and ongoing management, businesses can leverage this functionality to achieve their operational and financial objectives while maintaining the flexibility needed for future growth and adaptation.
Keywords:



